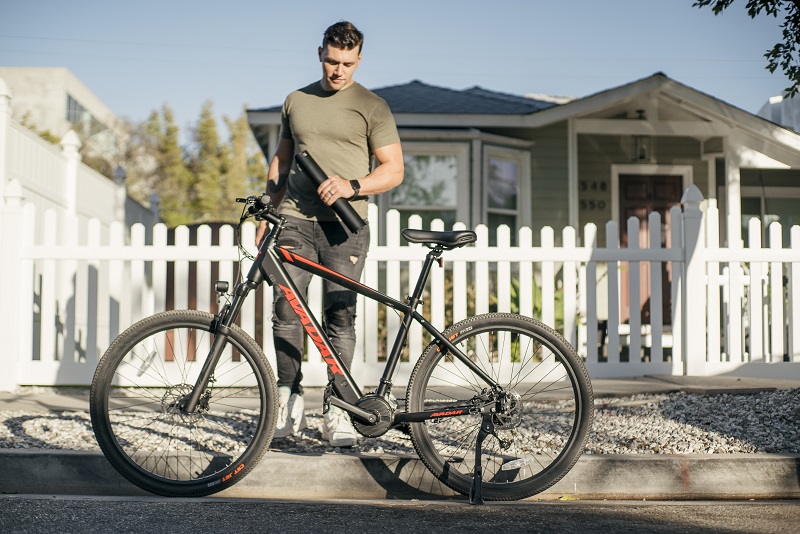
Why Are the 18 Bicycle Riding Rules of 1942 Still Being Adhered To
The coolness of the wind, the passing landscape, and the right bicycle bring you a different life.
But in sports there are always bumps, bruises, fractures and even death is an issue that can never be avoided, so in sports, we must always think about safety.
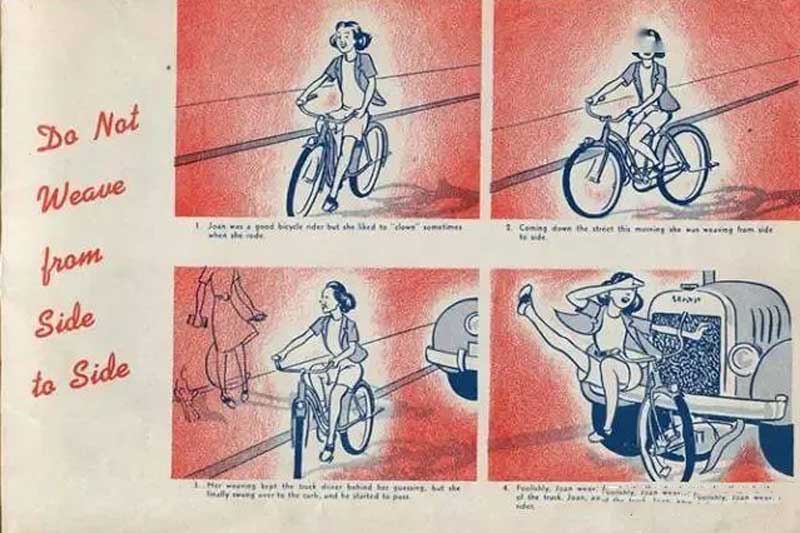
A group of illustrations published in the American Bicycle Club’s official safety manual in 1942 reminded everyone that safety awareness must always be remembered.
1. Do not weave from side to side

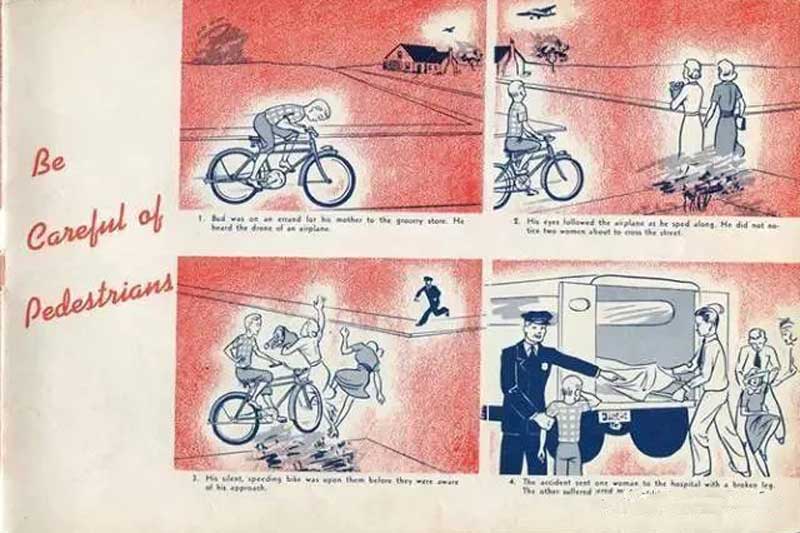
2. Observe all highway 'STOP' signal
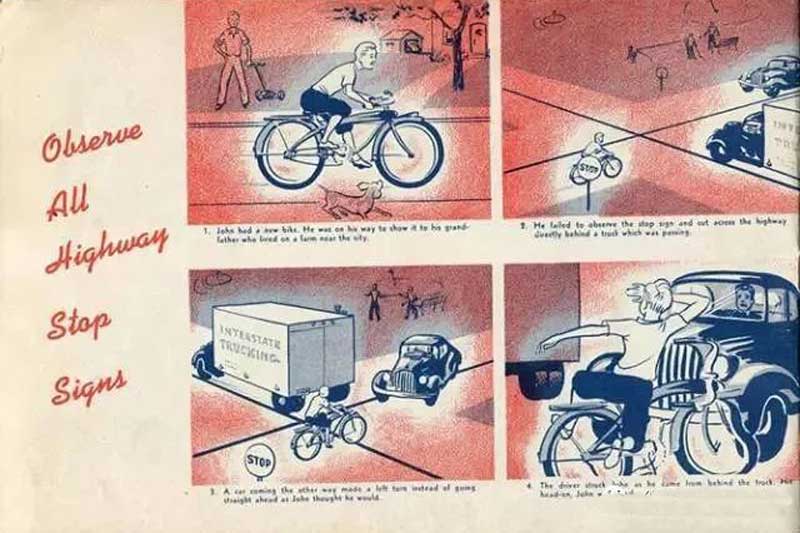
3. Be careful of pedestrians
4. Do not ride in the middle of the street

5. Be careful in parks

6. Keep a safe distance behind vehicles

7. Do not talk while riding

8. Look carefully before entering a street

9. keep bell on down in working condition

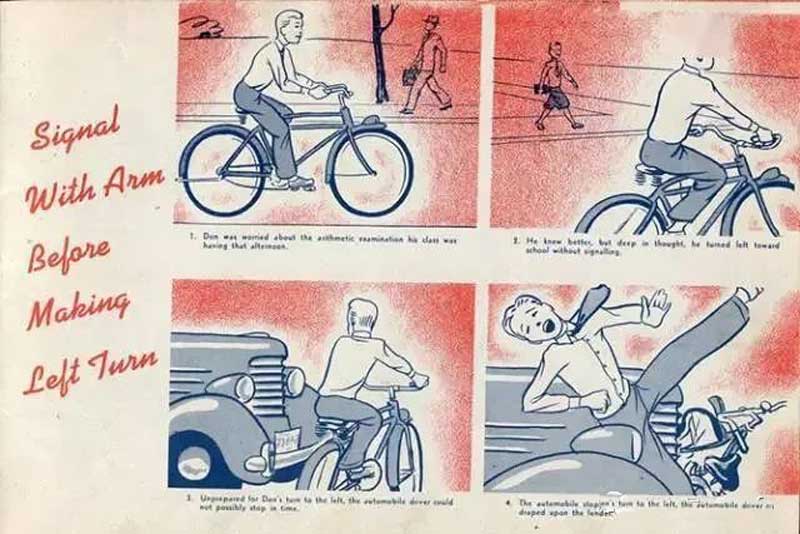
10. Signal with arm before marking left turn
11. Do not pass moving vehicles on the right

12. Do not carry passengers on handle bass

13. Keep your eyes on the road

14. Trick riding is dangerous

15. Always ride in single file on highways

16. Do not ride on sidewalks

17. Do not ride through red lights

18. Racing on the streets is dangerous

What is an Electric Bike?
What is an Electric Bike?
If you have never seen an e-bike before, it may be hard to imagine exactly what it looks like or how it differs from a regular bike.
E-bikes are just like regular bicycles, except they have a compact electric motor that gives you a boost of energy as you climb hills or ride long distances.
If you have a particular taste in bicycles or need a bike for a specific type of ride, you can be sure that there is an e-bike for you. E-bikes come in different shapes and sizes to suit different needs, whether you need an efficient e-bike for your morning commute or an extreme model for rough terrain.
Even though e-bikes are becoming more popular lately, they are not a novelty. Prototypes of electric bikes date back to the late 19th century. This means that around the same time that Karl Benz patented the first commercially available car, other inventors were working to improve the speed and power of bicycles. One inventor in particular – Ogden Bolton – filed a patent for what may have been the world’s first electric bicycle in 1895. Thanks to inventors like Bolton, e-bikes are now available to all.
How do electric bikes work?
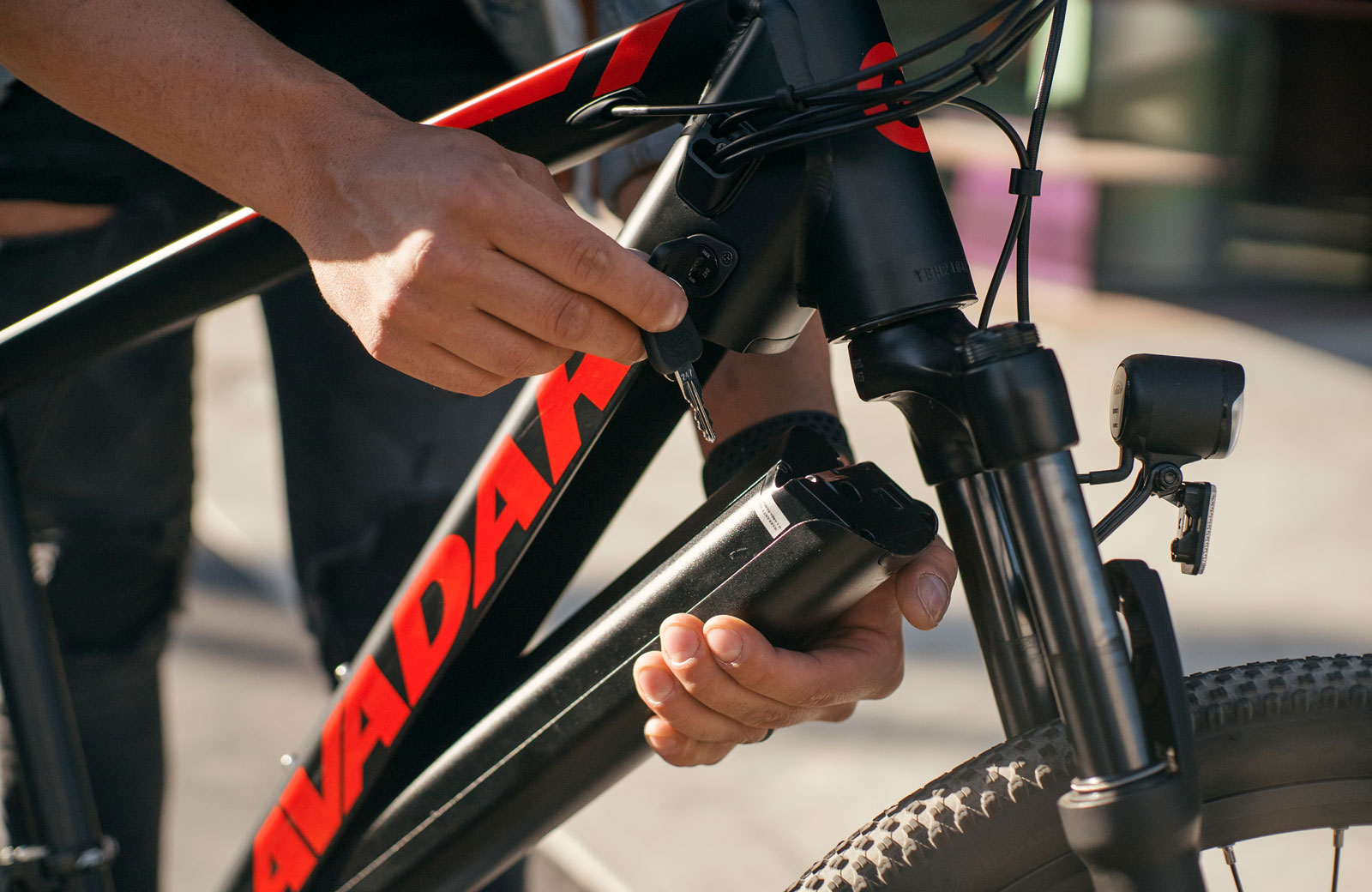
E-bikes work just like conventional bikes in terms of pedaling, but unlike traditional bikes, they have a battery and a motor. The battery stores the energy to power the motor. The motor is compact and built into the hub of the rear or front wheel, or mounted in the center of the bike. The motor is the component that drives the wheels.
In addition to the battery and the motor, another important component of an e-bike is the speed sensor or torque sensor. A speed sensor, also called a cadence sensor, automatically tells the motor to start as soon as you start moving. A torque sensor, on the other hand, helps you match your power whether you are going slow or fast. With a torque sensor, the harder you pedal, the greater the assistance. A speed or cadence sensor detects whether you are pedaling, and a torque sensor measures how hard you are pedaling.
Do you still need to pedal on an electric bike?
Part of what makes an e-bike so fun and healthy is that you can pedal whenever you want – it’s totally up to you. The battery and motor help you tackle inclines, rough terrain, or long distances, so you can keep cycling and move without overexerting yourself. So, with an e-bike, you are still riding a bike, but you are riding faster and less strenuously than with a traditional bike. When you need a break, you can choose to ride on the throttle, where you do not have to pedal and enjoy the breeze while you ride along your favorite trail.
Overall, you have a lot of flexibility with an e-bike. If you want to ride uphill like a traditional bike, you can turn the e-bike off and turn it back on whenever you want. If you do not feel like riding uphill, your e-bike is ready to assist you. Our bikes have 5 levels of assistance.

How much does an electric bike cost?
The cost of an electric bike varies and depends on what trips you plan to take and how often you plan to use your bike. If you plan to replace your car with an electric bike and commute to work, it’s worth buying an e-bike with better features and a larger battery for a longer range. If you plan to use your e-bike mostly for relaxed leisure activities, you should choose a model that is easy on your budget.
Regardless of which model you choose, an e-bike is much less expensive than buying and maintaining a new car and can be an extremely economical choice if you plan to use your bike for regular trips. The average cost of a car is $36,590, not to mention the added costs of regular maintenance, registration, and insurance, according to Kelley Blue Book analysts. Whether you choose a higher-end bike or a more practical e-bike, you’ll still save a lot of money compared to a car. Take a look at the absolute best value mid-drive C3 electric bike in the United States.
Is an electric bike worth it?
Electric bikes tend to be more expensive than traditional bikes, but they offer everyone the ability to bike wherever they want to go. With an electric bike, you save money on gas, car maintenance, and car insurance, and you contribute to your health – so it all comes down to what it’s worth to you.
Should I buy an electric bike?
E-bikes are a great option for people who have trouble going up hills, want to travel longer distances, struggle with various physical limitations, or would otherwise benefit from a little assistance. Take a look at our mid-drive electric bikes.
How to Choose an Electric Bike
When you ride an electric bike – or e-bike – for the first time, it can feel like discovering a superpower. That’s because pedal-assist e-bikes expand your options on two wheels: you can keep up more easily in stop-and-start traffic, arrive at your destination less sweaty, or simply enjoy a little more momentum on rides that might have otherwise seemed too far or too hilly.
E-bikes initially fall into the same categories as conventional bikes: mountain bikes and road bikes, as well as niches such as city bikes, hybrid bikes, cruisers, cargo bikes, and folding bikes.
Understanding the Three Classes of Electric Bikes
Primarily for regulatory reasons, electric bikes are also divided into classes that indicate their level of motor assistance. The question of which class of e-bike you need is an important decision point:
-
Class 1: Motor turns on only when you pedal and stops helping at 20 mph.
Class 2: Also has pedal assist up to 20 mph and a pedal-only mode.
Class 3: Pedal assist only (same as for Class 1), but the assist continues until you reach 28 mph.
Most new cyclists start with a Class 1 e-bike. Class 1 bikes are the most affordable and, in terms of regulatory requirements, the most widely accepted. You can ride them on city streets and many bike paths.
Class 2 e-bikes are generally allowed in the same locations as Class 1 e-bikes. This is because both classes have a maximum speed of 20 mph for motor assistance.
Class 3 e-bikes are popular with commuters and walkers. Compared to Class 1 bikes, they are faster and more powerful (and cost more). The benefit of this added power is that you can better keep up with traffic. They also climb better and can carry heavier loads. The downside is that you cannot ride on most bike paths or mountain bike trail systems.
Find out the access rules before making a final decision on an e-bike class. The caveat with all of the above access information is that laws, licenses, registrations, age restrictions, and land management rules change.
E-bike batteries, ranges, and motors

Manufacturers pay a lot of attention to the drive system of any bike. The tradeoff in development is power versus range. A more powerful motor provides more speed to keep up with traffic and more torque to climb hills and carry loads. A more powerful motor also consumes the battery faster, reducing your range.
If you compare potential e-bikes, you’ll see a broad range of specs: 10-60 miles with pedal assist, for example. That’s because so many variables affect range.
Battery charging time: most batteries take three to six hours to fully charge, with large capacity batteries taking longer. You can purchase an additional charger (or take your charger with you) if you plan to commute on your e-bike. You can also buy faster chargers.
Multiple batteries: Some e-bikes allow you to use two batteries at the same time. This can extend the duration of your ride – and if one battery dies, you have a backup. You can also buy an extra battery to have a fully charged one on hand or to replace your battery at the end of its life (usually several thousand charges).
Battery installation: Batteries integrated into the frame make room for bottle cages or a small bike bag. External batteries, however, are easier to charge and replace.
Mid-drive motors are located at the bottom bracket (the place where the crank arms attach to the bicycle frame). Hub-drive motors are located in the hub of the rear wheel (some are located on the front wheel).
Mid-Drive Motors: Many motors are equipped with this system for a variety of reasons. The pedal assist responds with a natural feel, and the weight of the motor in the mid and low provides a balanced and stable ride. Take a look at our mid-drive bikes.
E-bike Motor Torque

Torque is a specification you should check if you plan to drive uphill a lot and/or carry heavy loads. Measured in Newton-meters (Nm), the stated maximum for an e-bike is between 40 Nm and 80 Nm. However, your actual riding torque will vary if you change the pedal-assist settings.
Make sure your e-bike fits well
Another truism for both regular bikes and e-bikes is that the best bike for you is the one that truly fits you. For an investment as big as an e-bike, make sure it feels like it was made for you – or that it can at least be modified to fit you with a few clever replacement parts – before you ride it out the door.
The most important thing for a good fit is to know what frame size you need, which is roughly based on your body size. Aside from frame size, the frame geometry of an e-bike determines how it should fit your body measurements. A visit to a bike shop is the best way to adjust your fit so that your knees, shoulders, back, feet, and hands are properly aligned for the riding position you desire. You can also visit a specialist to get a detailed bike fitting that can prevent chronic injuries and help you perform at your best.
When you are in a bike shop, take the time to test ride the bike you want. Most stores have a room where customers can do this. Trying more than one bike will give you a better feel for your options and help you figure out which style is best for you.
Electric Bike Battery Health – Do’s And Dont’s
Charging Your Battery
Be sure to close the rubber charger port cover after disconnecting your charger.
If contaminants or moisture enter the charging port, it can destroy your battery and pose a safety risk!
When inserting the charger tip to your battery’s charging port, be careful, there should not be excessive weight on the charging tip from the wire or charger’s black box.
Do not wiggle the charger tip inside the charging port of the battery.
Battery Longevity
Our batteries are rated for 800-1000 charge cycles. One cycle is counted as charging the battery from 0 percent to 100 percent. Take good care of your battery and this means if you charge your bike twice a week on average, your battery should last you 4-5 years! We all ride differently and may charge more or less than 2x a week – you do the math :
To maximize battery life, there are some things you want to do, and there are some things you definitely don’t want to do!
Battery Care – What to do
Try to keep the battery above 20% in general, your battery will be much happier. Charge the battery just to 80% when you can help it. Think of it like being hungry: Don’t wait until you are starving to eat; and when you do eat, don’t fill up to the point of not being able to eat anymore.
Keep your battery between the 20-80% charge level. This simple rule can increase the effective lifetime of your battery. You can set a timer on your phone or use an outlet timer. Typically for 1-2 hours, as the battery will likely get to the suggested amount in the first few hours of charging.
Nurture your bike and your battery! Failing to keep your battery charged or forgetting to use your bike/check the battery levels consistently (monthly at minimum) is a sure fire way to damage your battery and kickstart the L-ion cell degradation process. Batteries are expensive and ensuring to do this will keep a smile on your face and more money in your pocket!
If storing for longer periods, it is a good idea to store your battery with a 40-80% charge. Check the battery once a month. If the battery drops to 20% or below, charge it up to the 40-80%. Recommended storage temperatures are 50F – 77F. Storage should be done in a dry area.
Battery Care – What not to do
You actually want to avoid charging to 100 percent and as this can stress the battery. It is better to charge to 80 percent if you know a full charge is not needed. If you plan on doing a longer ride, charge the battery fully with the knowledge you will drain the battery from max capacity soon.
Do not leave the battery on the charger unnecessarily or for extended periods of time after the battery has been fully charged. Doing this can expedite battery cell degradation and reduce the lifespan of your battery significantly.
Pro Battery Tip – Avoid draining your battery completely. If your battery is nearly dead and your bike powers off, do not power the bike up or drain the battery any further. This can harm your battery and reduce its longevity over time. In this case, use leg power or wait until you get home to charge up the bike.
Avoid temperature extremes! Very hot or cold temperatures can negatively affect the performance of the battery and shorten its expected life. Avoid exposing the battery to extreme cold or heat for long periods of time. 40F- 90F are ideal operating temperatures.
Dry off your battery charging port after you ride in wet conditions and ensure that there is no moisture or debris on both the charger tip or the charging port before plugging in your bike to charge. Plugging in your battery while wet risks damage to the battery, charger, and the potential risk of fire or injury.
E-Bikes 101
Introduction: Your Electric Bike Buyer’s Guide
Do you wish you could commute to work on a bike, but don’t want to change from workout clothes to business casual the moment you arrive? Are you aching to get active and tackle steep hills but aren’t sure if your knees can handle the task? Do you want to find a more eco-friendly option for last-mile travel, but don’t have consistent access to e-scooters and e-bikes in your town?
Imagine cruising on a bike, powered by a motor, to work every morning without breaking a sweat, zipping up hills without wearing yourself out for the ride back home, or having fun and practical transportation alternative to reduce your carbon footprint. Electric bikes (e-bikes) make it possible for anyone in just about any shape, and just about every location, to enjoy the benefits of biking every day. The best part is that you’ll still get exercise, and you’ll have a blast! If you’ve heard of e-bikes, and are considering purchasing one for yourself, you probably have a ton of questions. You’ve come to the right place. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know before shopping for an electric bike so that you can buy it with confidence. We’ll answer questions such as:
- What is the best electric bike to buy?
- What do I need to know about buying an electric bike?
- Do you have to pedal an electric bike?
- Can you get fit on an electric bike?
- What should I look for in an electric bike?
- What regulations should I know about?
Buying an electric bike is a big decision and an investment in your health and quality of life. Whether you’re a mountain biking expert or a beginner biker looking to commute or simply cruise some scenic trails, there’s an e-bike for you. Biking e-style can help you reach health goals, enjoy the recreational aspect of biking, and rely less heavily on cars if you choose. Ready to join millions in a biking revolution? We’re here to help you get started. Read this electric bike buyer’s guide or contact us at Avadar Bikes, and we’ll be thrilled to answer your questions and provide tips.
CHAPTER 1 - How Does An Electric Bike Work?
Electric bikes are becoming more popular as a transportation and recreation option, and they are currently the fastest-growing type of bicycle on the market. For example, e-bike sales totaled over $77 million in 2017 – up 91% from 2016. People across the country are switching out cars for e-bikes to zoom past traffic or have a completely new biking experience. E-bikes are booming, and we can’t wait to show you why. But, first thing’s first — you need to consider if an e-bike is exactly what you need.
In this chapter, we’ll cover the basics to help you decide if an e-bike is right for you and your lifestyle. If you’re excited to browse bikes now, check out our selection of e-bikes for beginners or seasoned e-bike enthusiasts.
What Is An Electric Bike?
If you’ve never seen an e-bike before, it may be hard to imagine exactly what one looks like or how it’s different from a regular bike.
E-bikes are like traditional bikes except they feature a compact electric motor to provide a power boost for climbing hills or traveling long distances. E-bikes are not the same as mopeds or motorcycles, are not loud, and don’t give off emissions.
If you have a particular taste in bikes or need a bike for a specific type of ride, you can be sure there’s an e-bike for you. E-bikes come in a range of shapes and sizes to suit different needs, whether you need an efficient e-bike for the morning commute or an extreme performer for rugged terrain.
Even though e-bikes are recently increasing in popularity, they aren’t something new. Electric bike prototypes date back to the late 19th century. This means that around the same time Karl Benz patented the first commercially available car, other inventors were working on improving the speed and power of bicycles. One inventor in particular — Ogden Bolton — filed a patent in 1895 for what may have been the world’s first electric bike. Thanks to innovators like Bolton, e-bikes are now available to all.
How Do Electric Bikes Work?
E-bikes work in the same way as traditional bikes as far as pedaling goes, but unlike traditional bikes, they feature a battery and a motor. The battery stores the power to drive the motor. The motor is compact and built into the hub of the back or front wheel, or mounted in the center of the bike. The motor is the component that spins the wheels.
Besides battery and motor, another important part of an e-bike is the speed sensor or torque sensor. A speed sensor, also known as a cadence sensor, automatically tells the motor to start once you start moving. A torque sensor, on the other hand, provides assistance to match your power, whether you’re going slow or fast. With a torque sensor, the harder you pedal, the greater the boost. Basically, a speed or cadence sensor detects if you’re pedaling, and a torque sensor measures how hard you’re pedaling.
Do You Still Have To Pedal An Electric Bike?
Part of what makes an e-bike so much fun and beneficial to your health is you can pedal whenever you wish — it’s completely up to you. The battery and motor provide a boost to help you bike up hills, over rough terrain, or cover long distances, so you can still bike and get exercise without overworking yourself. So, with an e-bike, you’re still biking, but you’re enjoying a faster, less stressful biking experience than you would with a traditional bike. If you decide you need to take a break, you can opt for throttle-only riding which doesn’t require pedaling, and enjoy the breeze while you speed down your favorite trail.
Overall, you have great flexibility with an e-bike. If you want the challenge of trekking uphill as you would with a traditional bike, you can turn the power off an e-bike, and switch it back on whenever you want. If you’re not in the mood for hill climbing, your e-bike will be ready to assist you.
Some e-bikes provide different levels of pedal assist to suit your needs. For example, Avadar Bikes offers ECO mode, which provides less power and helps the rider save more of the battery charge. A higher pedal assist level, like level 3, provides greater power to help you cruise up to 20 mph. The different power levels can be used to help you adhere to the local e-bike speed laws.
How Much Does An Electric Bike Cost?
The cost of an electric bike varies and depends on the riding you plan to do, and how often you plan to use your bike. If you intend to replace your car with an electric bike and commute to work, it’s worth getting an e-bike with more premium features and a larger battery for an enhanced riding range. If you plan on using your e-bike mostly for laid-back recreation, you might feel comfortable finding something that’s easier on your budget.
To give you an idea of what to expect, the average cost for an electric bike ranges between $2,000 and $3,000. Avadar electric bikes range from $1,980 to $2,380. Our practical C3 is great for beginners and costs $1,980.
No matter which model you choose, an e-bike is much less expensive than the cost to purchase and maintain a new car and can be an extremely economical choice if you plan on using your bike for regular transportation. The average cost of a car is $36,590, not to mention the added costs of regular maintenance, registration, and insurance, according to analysts at Kelley Blue Book. Whether you choose a higher-end bike or a more practical e-bike, you’ll still save big on costs compared to a car.
Is An Electric Bike Worth It?
Electric bikes typically cost more than traditional bikes, but they offer a way for anyone to bike wherever they need to go. With an electric bike, you’ll save money on gas, car maintenance, and car insurance as well as contribute to your health, so it’s what it’s worth to you.
Should I Buy an Electric Bike?
E-bikes are an excellent option to empower people who struggle to bike up hills, desire to ride for longer distances, are dealing with various physical limitations, or who would otherwise benefit greatly from a little boost.
They also make great alternatives to a car for those who want to avoid commuter traffic and enjoy a healthy ride to start their day right, while reaping the benefits of biking. E-bikes are incredibly fun and pretty much guaranteed to put a huge smile on your face!
Whether or not you should buy an e-bike is ultimately up to you. If biking is something you enjoy or if you’re interested in a fun way to improve your health and the environment, we say it’s certainly worth considering.
If you have more questions or want to speak with one of our team members, contact us today. We’ll be happy to share our knowledge with you, so you know exactly what to expect when you ride an e-bike for the first time.
CHAPTER 2 - What Will You Be Using Your Bike For?
One of the greatest factors you’ll need to consider when choosing an e-bike is what you’ll be using the bike for. Do you want to get fit, or is your goal to become less reliant on a car to get around – or both? In this chapter, we’ll answer your questions about e-bike uses and the benefits of riding an e-bike. If you’re still not sure if an e-bike is right for you, contact our team, and we’ll be happy to answer your questions.
Using An Electric Bike To Get Fit
E-bikes get riders where they need to go faster than traditional bikes, increase convenience and decrease physical fatigue. Plus, riding an e-bike is just plain fun! You can still pedal an e-bike, so that means you still get exercise and can improve your health. E-bikes simply assist you as you bike, but they don’t take over completely, and you can always pedal faster or turn the power off when you want to increase your heart rate.
More people want to bike, and e-bikes eliminate many of the common complaints people have about riding traditional bikes. According to a PeopleForBikes survey, half of the American adults want to ride bikes more often. Many people don’t ride bikes as much as they’d like to because they don’t have access to biking infrastructure. Another reason people avoid biking is comfort. People don’t want to arrive at work sweaty and tired, but e-bikes can help workers comfortably commute and get fit at the same time. E-bikes remove other obstacles that have prevented people from biking in the past, such as helping riders go longer and faster without putting extra stress on their joints.
Riding an e-bike is a great way to get started on a fitness plan. Most of all, using an electric bike motivates people to get fit. For example, according to a National Institute for Transportation and Communities (NITC) survey, out of 6.6% of adults who did not traditionally ride as an adult, almost 94% ride weekly or daily with an e-bike.
Even if you regularly ride bikes or are in excellent shape, you’ll ride longer with an e-bike and reap the health benefits. The majority of all respondents in the NITC survey, including adults who regularly rode bikes before purchasing an e-bike, ride more than they did with a standard bike because an e-bike is fun. Also, fit individuals can ride as they recover from the prior day’s workout. Use your e-bike as a means of transportation, and combine your power with the bike’s power, and you’re bound to see results.
Is Riding An Electric Bike Good Exercise?
Although an e-bike provides some assistance, regularly riding an e-bike provides an effective workout, especially for those who are otherwise sedentary.
A study published in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity found evidence that e-cycling provides physical activity of at least moderate intensity, which is lower than conventional cycling but higher than walking.
A University of Colorado study found that e-bike riders experienced improved cardiovascular health after just a month of riding 40 minutes a day, three days a week. Therefore, e-bikes can improve cardiorespiratory fitness.
E-bikes provide a pleasurable way to exercise too, so riders look forward to getting outside and going for a ride. Motivation is key to sticking to an exercise routine. With an e-bike, you can easily replace driving with cycling, and fit in exercise throughout the day where you wouldn’t have exercised in the past.
Ultimately, you control your bike workout and can adjust assist levels to increase or decrease intensity to help you reach specific goals.
Using An Electric Bike To Commute
According to the NITC survey, one of the top reasons people buy e-bikes is to replace car trips. There are tons of benefits to commuting to work by e-bikes, such as saving money on car-related expenses, improving health, avoiding traffic, decreasing stress, avoiding parking hassles, and decreasing emissions.
Imagine the beauty and freedom of whooshing past motorists stuck in the morning jam, and being able to find a parking space the moment you arrive. And, if you’re not in the mood to hit the gym after a long day of work, there’s no need to feel like you sabotage your health. When you use an e-bike to commute to and from work, you can relax at the end of the day knowing you already did your health a favor — no gym membership required.
If you already commute to work by bike, switching to an e-bike will get you there faster, and you’ll arrive cool, collected, and ready to let your talents shine.
What Is The Best Electric Bike For Commuting?
The best e-bike for commuting depends on your needs.
To choose the best e-bike for your commute, consider the following factors:
- The length of your commute: The length of your commute will help you determine your comfort, speed, and battery range requirements. For example, if your workplace is only 3 miles from where you live, you can be a lot more flexible with the type of e-bike you choose because you don’t have to go very far. On the other hand, if you need to ride 9 miles to work every day, you’ll want something that’s designed for speed, comfort, and efficiency. Considerana Avadar 3 electric bike with a 52-volt (V) battery because this type of e-bike will go up to 28 mph, with a 40-plus mile riding range, and will help you get to work on time without any anxiety about running out of battery charge.
- The climate: What is the weather typically like where you live and work? Do you see a lot of precipitation where you live? If it rains a lot in your city, for example, you may want to choose a bike with wider tires rather than a typical commuter bike with large narrow tires. Make sure to consider how your e-bike will handle the weather where you live.
- Brake requirements: Will you need to do some heavy braking during your commute, or do you plan on cruising quiet back streets to get to work? If you need stopping power, precise braking, and brakes that perform well in wet weather, aim to choose a commuter e-bike with a quality hydraulic brake system.
- Topography: Consider the land features of your commute, and what you’ll need to bike through every day. If you live in a hilly area, for example, and want a basic e-bike that’ll reduce your effort as you go up hills, you should be fine with a Class 1 bike.
- Battery range requirements: Consider how many miles you’ll be traveling to and from work to choose an e-bike with the right range — or how far you can ride on one battery charge.
Lastly, consider if you want your e-bike to include space for a laptop, bag, or groceries. If so, look for an e-bike that comes equipped with a rack for additional storage capacity.
How Much Faster Is An Electric Bike?
The average cycling speed on a traditional bike for city riding is 11 to 12 mph. With an e-bike, you can go almost twice as fast with less effort because you can hit 20 or 28 mph before the pedal assists stops.
What Are The Benefits Of Riding An Electric Bike?
There are tons of reasons e-bikes are growing in popularity, and will likely continue to replace cars and traditional bikes. Here are some of the benefits of being an e-bike owner and reasons to feel good about enjoying your new ride:
- Greater control and cycling power: With an e-bike, you don’t give up any of the control you had with a traditional bike, but you do increase your power. You get to choose when or when not to use the pedal assist or throttle. You get to go up hills with an extra boost and without exhaustion. E-bikes put you in complete control of your biking experience.
- Time-saving speed: E-bikes provide the boost you need when you’re running short on time or want to experience more of a rush.
- A more enjoyable ride: Long rides can be rough even for the fittest individuals. An e-bike reduces the fatigue resulting from riding harder and longer and lets you make the most of your bike ride.
- Can increase fitness: E-bike owners look forward to riding and are more likely to bike and get the exercise they need. Whether you need to get or stay fit, an e-bike is a fun way to stay on track.
- Can ride in hilly areas: Hilly terrain does not need to keep you from biking when you own an e-bike. As an e-bike owner, you can zip up and down hills and still enjoy the physical and mental benefits of biking.
- Can bike without breaking a sweat: Going to work, a job interview, or an important meeting? With an e-bike, there’s no need to pack an extra set of clothes. The pedal assist will allow you to reach your destination on time without breaking a sweat.
- Save money on car expenses: Cars and car-related costs are financially draining. With an e-bike, you can take a break from the headache of maintaining a car and save money for other things you want to enjoy in life.
- Reduce your carbon footprint: The typical vehicle contributes an estimated 6 to 9 tons of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere each year. One way to drastically reduce your carbon footprint is to bike more often. Riding an e-bike, which does not emit any gases, is a fun and easy way to reduce your carbon footprint.
- Skip rush hour traffic: Have you considered quitting your job just to avoid rush hour traffic? Before you call it quits and move somewhere else, try commuting to work on an e-bike and get ready to kiss rush hour traffic goodbye.
- Makes biking accessible to those who couldn’t bike before: If certain medical conditions have prevented you from biking in the past, consider an e-bike to reduce the stress traditional biking puts on the body. E-bikes make biking possible for individuals with joint issues or who need to ease into a fitness plan.
- There are e-bikes available to meet your needs: E-bikes are available in many shapes and forms, just like traditional bikes. So, if you think all e-bikes are designed just for experienced cyclists, think again. Just reach out to us, and we’ll help you find what you need.
- They’re quiet: Are you envisioning a loud bike zipping around a quiet neighborhood, waking up the neighbors? E-bikes are not to be confused with motorcycles and sports cars, even though they’re fun to ride at full speed. E-bikes are quiet, and won’t disturb the peace of your community or your blissful ride.
CHAPTER 3 - Where Will You Be Riding?
Another factor to consider when selecting an e-bike is where you’ll be riding. Do you plan to mostly cruise country roads, zoom down urban lanes or go off-roading in the mountains?
In this chapter, we’ll explore the differences between e-bikes for on and off the road. We’ll also look at e-bike regulations to help you prepare for a safe ride. If you’re not sure which bike suits you, contact us at Avadar Bikes and we’ll help you find the best e-bike for your terrain.
Electric Bike Regulations
E-bikes are regulated by the Consumer Product Safety Commission for the sake of product safety. This means that the federal government only regulates the condition of an e-bike for sale, and not how it’s used. Federal law defines an e-bike as a low-speed electric bicycle with fully operable pedals and an electric motor of fewer than 750 watts, and which does not go faster than 20 mph when powered only by a motor. Federal law does not specify the max speed for traveling using a combination of human and motor power.
To know the e-bike laws that apply to you, you have to check with your state. State traffic laws vary and determine how e-bikes can be used within the state. The majority of states define electric bikes in their traffic laws, but some states do not. Also, some states have specific laws that apply only to e-bikes. For example, some states require a license to operate an e-bike. Other states apply the same laws to e-bikes as traditional bikes. A good place to learn about the e-bike laws in your state is to click on your state at Peopleforbikes.org.
Can You Ride An Electric Bike On The Sidewalk?
Like e-bike laws in general, bike sidewalk laws also vary by state and local governments. For example, New York does not have a statewide law prohibiting sidewalk bike riding, but a person cannot ride a bike on a sidewalk in New York City unless permitted by a sign. To look up your state laws regarding sidewalk riding, check out your state on Bikeleague.org.
What Age Can You Ride An Electric Bike?
Age restrictions also vary by state. For example, in California and Utah, an individual under the age of 16 may not operate a Class 3 electric bike. Arizona, Idaho, and Wyoming have no age restrictions to ride any class of e-bike.
CHAPTER 4 - How Far Will You Be Riding
You’ll need to know how long you plan to ride before choosing an e-bike. Will you be biking a short commute, or do you often like to bike miles upon miles of trails? Knowing what range you need will help you select the right battery. You’ll also know what to expect so you can plan your bike trips accordingly.
In this chapter, we’ll cover everything you need to know about e-bike batteries so you can hit the road worry-free and well prepared for the ultimate ride.
Electric Bike Battery Types
The battery is an important part of what makes an e-bike so enjoyable.
With a fully charged battery, you can cruise with the wind care-free. When the battery loses its charge, you can still pedal, but you’ll miss out on the e-bike fun.
Here are the different types of e-bike batteries:
- Lead-acid batteries: Lead-acid batteries are low-cost and easy to recycle, but are heavy and do not last very long. They are similar to the batteries used in cars.
- Nickel-cadmium batteries: Nickel-cadmium batteries last longer than lead-acid batteries but are difficult to recycle.
- Nickel-metal hydride batteries: Nickel-metal hydride batteries last longer than nickel-cadmium batteries and are easier to recycle, but generally offer the same performance.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion batteries last longer than the other batteries and generate more power. These types of batteries use the same technology as cell phone batteries.
Which Battery Is Best For An Electric Bike?
In general, the best type of battery is a form of lithium-ion battery. They are smaller and last longer than lead-acid batteries.
When considering batteries as you shop for an e-bike, consider watt-hours (Wh) which measure battery output and life. The higher Wh, the bigger the range. Aim to choose a bike that offers a range long enough to suit the length of your ride with the power level you need. Lastly, consider how long it takes to recharge the battery and how that fits into your e-bike goals.
How Long Does the Battery Charge Last?
How long a battery lasts depends on several different factors, including the battery power and the level of assistance you use. Any pedaling decreases battery to use and extends your range. Generally speaking, you can expect anywhere from a 25- to 70-mile ride on a single charge.
For example, through our range test, we found that on the bike with level 3 pedal assist, the range increased to 77 miles at 10 mph.
The overall life span of a battery depends on the type of battery. Lead-acid batteries typically last 200 to 300 charge cycles, while lithium batteries last from 500 to 1,000 charge cycles.